|
4.01 An airport is
(1) an aerodrome with paved runways.
(2) an aerodrome with a control tower.
(3) a registered aerodrome.
(4) a certified aerodrome.
4.02 A dry Transport Canada standard wind direction
indicator when horizontal indicates a wind speed of at least
(1) 25 KT.
(2) 15 KT.
(3) 10 KT.
(4) 6 KT.
4.03 No person shall operate any vehicle on any part
of an uncontrolled airport used for the movement of aircraft, except in accordance
with permission from
(1) the operator of the airport.
(2) the airport security officer.
(3) a federal peace officer.
(4) a qualified flying instructor.
4.04 Runways and taxiways or portions thereof that
are closed to aircraft are marked by
(1) red flags.
(2) horizontal red squares with yellow
diagonals.
(3) a white or yellow X.
(4) white dumb-bells.
4.05 The west end of a runway oriented east and west
is numbered
(1) 09.
(2) 90.
(3) 27.
(4) 270.
4.06 Refer to Appendix: HOLDING POSITION MARKINGS
(Diagram #1)
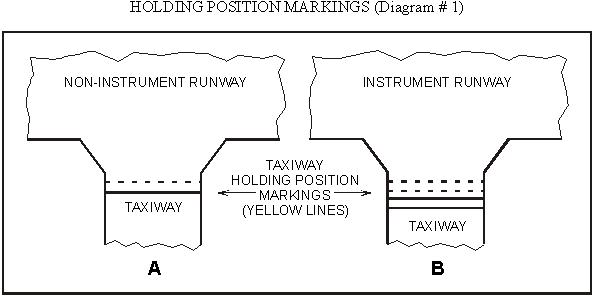
At controlled airports, the taxiway
holding position markings in diagrams A and B indicate that aircraft shall
stop
(1) on the solid line side at all
times.
(2) on the solid line side unless otherwise cleared by ATC.
(3) before crossing the lines from
either side at all times.
(4) before crossing the lines from
either side unless otherwise cleared by ATC.
4.07 Where taxiway holding positions have notbeen
established, aircraft waiting to enter an active runway should normally hold
(1) clear of the manoeuvring area.
(2) 50 feet from the edge of the runway.
(3) 150 feet from the edge of the
runway.
(4) 200 feet from the edge of the runway.
4.08 The manoeuvring area of an airport is that area
(1) normally referred to as the ramp
or apron.
(2) which includes the apron, taxiways
and runways.
(3) used when taxiing to and from
the parking area.
(4) used for taxiing, taking off and landing.
4.09 Except for the purpose of taking off or landing,
an aircraft shall not be flown over an aerodrome at a height of less than
(1) 2,000 feet AGL.
(2) 1,500 feet AGL.
(3) 1,000 feet AGL.
(4) 500 feet AGL.
4.10 Refer to Appendix: HELIPORT MARKINGS (Diagram
#1)

Select the helicopter ground markings which identify respectively
- a hospital heliport,
- a heliport.
(1) D, C.
(2) D, A.
(3) B, C.
(4) A, B.
PSTAR Questions:
Previous
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Next
PSTAR Commentary:
Previous 1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Next
This page written 8 October 2002 by Robyn Stewart. Last
revised 8 October 2002. |
Robyn's Flying
Start Home

Other Student
Pilot Resources
What Canadian student pilots
need to know
PSTAR
References
Links and how to use the A.I.P. the CARs and the CFS
Transport
Canada Exam Guides
Study guides and flight test standards
First Solo Requirements
Everything that needs to be completed before the first time you fly an airplane
by yourself
Search
Search all of wabyn.net
Contact Robyn
Send me e-mail
|